Ubuntu derivatives are the customized or forked builds of the original Ubuntu operating system developed by Canonical. When it comes to choosing the best user-friendly distribution of Linux, everyone will suggest Ubuntu. Since the initial release of the first public version in 2004, Ubuntu rose higher and higher with its popularity.
Ubuntu is considered one of the most stable and beginner-friendly Linux distribution. Before the era of Ubuntu, many people had a misconception about Linux. The terminal commands and all that stuff seemed nightmare to them. But nowadays, anyone with basic knowledge can run almost any desktop distribution of Linux since many distros followed the same path as Ubuntu.
But the matter is that there is no distribution of Linux, including Ubuntu, that is perfect or nearly perfect. Whether you are a power user or not, you will always wish the operating system was meant only for you. For this reason, the open-source community and avid Linux geeks have come up with the customized flavors or variants of a particular Linux-based operating system.
Among the Ubuntu community, these custom variants are known as Ubuntu derivatives. They provide a customized experience for every type of user. For example, if you have a potato PC that can barely run a full-fledged Ubuntu, you can go for a lightweight variant. Again, if you are a researcher in a particular field, you can get a derivative that is preloaded with all the state-of-the-art analysis tools.
Best Ubuntu Derivatives Worth Checking Out
There are almost a hundred Ubuntu derivatives available here and there on the internet. Some of them are official forks by Canonical, which they call “flavors.” But most of the derivatives or flavors are developed by indie developers who are the supporters of the open-source movement.
You should be extra careful for the abundance of Ubuntu-based custom Linux distributions before choosing a distro for your primary computer. Some of them have instabilities and bugs that can break your important files and expose your privacy. Here we have tested out and listed the 10 best derivatives of Ubuntu that you can check out and use without any doubt.
1. Linux Mint
You may disagree with the fact that Ubuntu is the best distro for light users. But I am sure that we both will agree on the fact that Linux Mint is the most popular and widely used Ubuntu derivative out there. This Linux distribution was built upon the foundation of Ubuntu and the veteran Debian OS.
This project is completely free and open-source. The Linux Mint community is constantly working to improve this distribution further. This distribution is especially known for its out-of-the-box multimedia support. People with a little knowledge about Linux can use this tool in their low configuration home computers, such as media centers.
Key Features of Linux Mint
- It uses Cinnamon as the stock desktop environment, although it comes with some other desktop environments if you want to check them out.
- It comes preloaded with many free and open-source software packages that are used, especially for multimedia purposes.
- It uses a custom application store named Mint Software Manager for installing different application software and addons on this distribution.
- It provides a clean and clutter-free user experience that needs less processing power compared to other distributions.
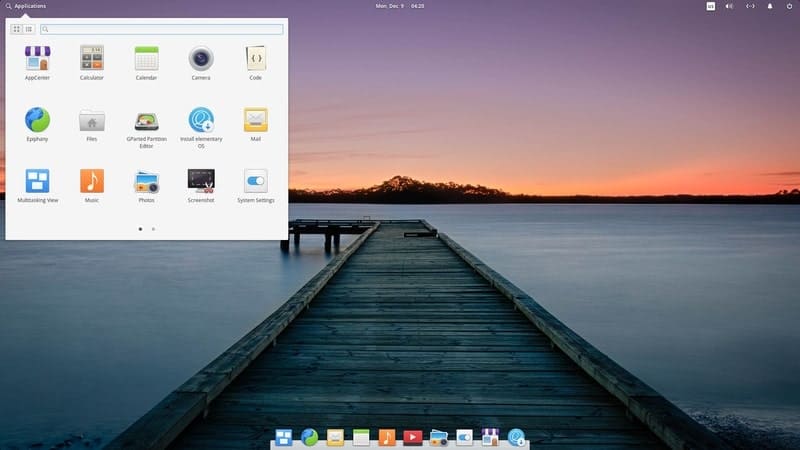
2. Elementary OS
Once, the Elementary OS was the most beautiful Ubuntu-based operating system. Although nowadays many operating systems have an aesthetically pleasing user interface, Elementary is still a beautifully decorated distro. It derived many of its UI elements from the macOS. And, hence it had to face both praise and criticisms.
It is an open-source project, but it runs on a “Pay What You Want” model. Though Elementary is a design-centric operating system, it has a plethora of features that help to boost your productivity. Besides, protecting your privacy is a great concern for this project.
Key Features of Elementary OS
- It uses the Pantheon desktop environment as a default, and it supports a lot of features and customizations.
- The developers selected and included the best software and some of Elementary’s proprietary packages inside the distro package so that you can start straight out of the box.
- It uses its AppCenter for installing packages. Unlike other Linux app repositories, the Elementary team curates and maintains this store nicely.
- Elementary OS has a great storage manager that automatically keeps your storage free and protects against any private file breach.
3. Zorin OS
ZorinOS is a reliable operating system built upon the codebase of Ubuntu. However, it is heavily customized so that it doesn’t look and feel like Ubuntu. The user interface has a similarity with Windows and Mac operating systems. Unlike most other Linux distros, this is a paid operating system that requires a one-time purchase of the license.
But if you don’t want to spend any bucks, then there are several other free editions of this Ubuntu derivative, such as Core, Lite, and Education. These will offer you fewer features, and you won’t get access to many premium proprietary software packages developed for Zorin. The Ultimate Edition of this distro is not that costly, and it’s worth paying for if you want a solid user experience.
Key Features of Zorin OS
- You will get a complete set of features and customizations that are neatly arranged to give you the best user experience.
- The best applications for your workplace and home entertainment, along with several games, will be installed with the package.
- You can switch seamlessly between Mac, Windows, Ubuntu, and Classic GNOME layouts.
- Zorin Grid is an upcoming feature that will help you manage and control your organization’s workstations with ease of running their operating system.
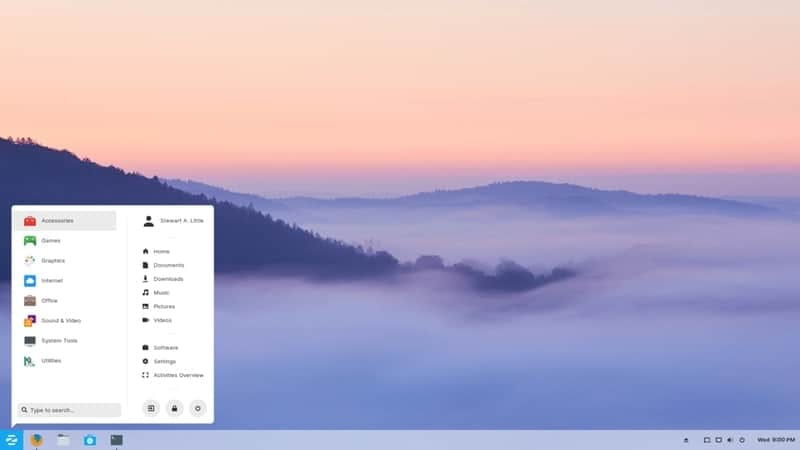
4. KDE Neon
KDE is a popular name in the world of free and open-source software. Their Plasma Desktop Environment and some other tools developed for Linux are very popular among the FOSS geeks. The KDE Neon is a customized Linux-based operating system that was built upon Ubuntu distribution.
It was initially announced in 2016, and that certifies that it a relatively new operating system. But it gained much popularity in this short span of development. Although KDE Neon uses the Long Term Release versions of Ubuntu, you will get all the latest system application packages straight from the KDE development community.
Key Features of KDE Neon
- There is an additional Developer Edition available for the open-source contributors to download.
- It is a gateway to the latest and hottest software and addons developed by the KDE Community.
- They have even released a laptop named Slimbook with preinstalled KDE Neon for providing you the best possible KDE experience.
- This distro uses their Plasma desktop environment that is used by default in some other beautiful Linux distros.
5. Pop!_OS
Unlike most other Linux distributions, Pop OS is not maintained by an open-source community. However, it’s a completely free and open-source Linux distribution built based on Ubuntu with several tweaks. System76 is the parent company that is originally known for building custom workstation rigs.
They built Pop OS for preinstalling it with their hardware as a free alternative to Windows to use right after unboxing. Since they made this distro publicly available, it gained much popularity. It is not just another Linux distro with some visual changes. Rather it provides some really useful features that are not available even with the stock Ubuntu.
Key Features of Pop!_OS
- Though Linux is not intended for gaming purposes, Pop OS provides many intuitive features and preinstalled games exclusively for gamers.
- It provides native support for the discrete GPU of your computers, such as AMD and Nvidia.
- It has a dedicated software store named Pop Shop that will allow you to install and uninstall the packages conveniently.
- You can use Pop OS with the developers’ own set of hardware to get the best possible experience and customer support.
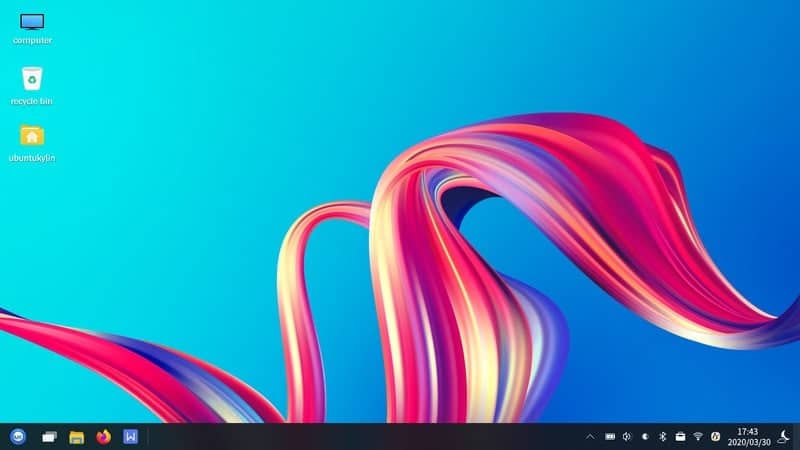
6. Ubuntu Kylin
It is one of Ubuntu’s very own official derivatives that are known as Ubuntu Flavours. This distribution is developed by Canonical for the Chinese people. The Chinese Ministry of Industry and Information Technology supports the development of this distribution. For this reason, some of you might not want to install it on your computer.
But for the people based in China, this is a very useful Ubuntu derivative. It is preloaded with China-specific software packages and features. The National University of Defense Technology of China and a supportive developer community of Kylin are constantly working to develop this distro.
Key Features of Ubuntu Kylin
- It uses Ubuntu Kylin Software Center as the default software repository to use additional repositories for installing packages.
- Many useful Chinese apps, input methods, addons are pre-installed with this distribution.
- This distro has native support for ARM-based chips that allow it to run efficiently on mobile devices.
- The default desktop environment for this distribution is known as UKUI, which is elegantly designed.
7. Linux Lite
Jerry Bezencon is the person who is leading the Linux Lite project. He built this distro by forking Debian and Ubuntu. The goal of the Linux Lite was to make it run on a very weak system with the taste of a modern user interface. The developer is calling it a “Gateway” towards Linux.
It is packaged with all the very lightweight applications. Besides, it trimmed out all the unnecessary clutter of the original Ubuntu that doesn’t provide much value to a beginner Linux user. This is an ideal operating system for those who are just thinking of ditching their precious Windows OS.
Key Features of Linux Lite
- The overall user interface runs swiftly and uses very little processing power unless you use any heavy tools.
- It has some lightweight system software preinstalled that is optimized to work with a few system resources.
- It provides out-of-the-box security and privacy protection with a built-in firewall and other features.
- Linux Lite has a great support community forum and built-in documentation for beginners.
8. Peppermint OS
Peppermint OS is yet another Linux distribution based on Ubuntu. The origin of this project is somewhat similar to the Linux Mint project. But the main difference is that the Peppermint OS uses the LXDE desktop environment by default. To make it suitable for low-end computers, the developers packaged it with several cloud-based application software.
This is why you can feel the experience of cloud desktop in this distribution. The exclusivity of these cloud apps that you don’t require to open a browser to run these apps. Rather a custom Firefox browser instance is kept running into the desktop for running these cloud apps just like native packages.
Key Features of Peppermint OS
- It has integrated the ICE tool that can turn any web app similar to a native package with ease.
- The Peppermint forum and official social media channels are very helpful towards new users.
- This distro is free from any bloatware, and the ICE-based cloud functionality makes it blazing fast and fluid.
- The latest version is built on the Ubuntu LTS and a stable Linux kernel, which is secure, reliable, and highly customizable at the same time.
9. Lubuntu
Lubuntu is a very popular Ubuntu derivative that is lightweight and uses the LXQt desktop environment as a default. This is also the reason for the “L” letter in the name. This distro is meant to be run smoothly on portable devices like a laptop that doesn’t require that much power.
This distro is a great starter pack for those who want to ditch their Windows system. Because the developers have included the necessary Windows tools alternatives with the installer package. Besides, you are getting some useful application packages from the LXQt family.
Key Features of Lubuntu
- It has its own Discover Software Center for installing reliable and trusted packages.
- This distribution is highly optimized for single-board computers, such as Raspberry Pi, OrangePi, etc.
- It features a wide range of customization options through the LXQt desktop, and the overall user interface is very neat and clean.
- The latest release is based on the Ubuntu Focal fossa LTS version, which is very reliable to use as the main workstation.
10. Xubuntu
Xubuntu is yet another official flavor of the original Ubuntu distribution. Just like its siblings Ubuntu Kylin and Lubuntu that I mentioned above, it resembles the features and looks of the mother, Ubuntu. Except it features the Xfce desktop environment for managing the workflow.
Though Canonical officially recognizes it as a part of their product family, this distro is mostly community-driven. The motive behind the development of this system is the same as Ubuntu, with the main priority on better usability and performance.
Key Features of Xubuntu
- Most of the useful work and entertainment apps are preinstalled so that you can start just after flashing.
- Though the stock look of the Xubuntu is very beautiful, you can customize it with your preferred desktop functionalities.
- The Xfce desktop environment is at the core that creates a good balance between workflow and aesthetics.
- It supports a wide range of packages and repositories that are also supported by Debian or Ubuntu.
Final Thoughts
Ubuntu itself is a great distro. You can customize it to anything you like. Even if you are a developer, you can build your very own derivative from the Ubuntu codebase. But this is not the case for most of the users. So, if Ubuntu cannot deliver you the best experience, any of the Ubuntu derivatives can do this for you.
There are some other great flavors of Ubuntu that are not included in the list. That doesn’t mean the other derivatives are not usable. It’s just because we have to finish the list at some point. If you still think that your favorite derivative or flavor of Ubuntu is missing in this list, then you can comment below with some of your favorite features of that distro. That would be helpful for many users who want to dive into the Linux world.











![10 exemples de commandes Gzip [Compress Files in Linux]](https://media.techtribune.net/uploads/2023/06/Gzip-Command-in-Linux-238x178.png)




